

 about
projects
people
publications
resources
resources
visit us
visit us
search
search
about
projects
people
publications
resources
resources
visit us
visit us
search
search
Quick Links
Recent Citations
Structural snapshots capture nucleotide release at the μ-opioid receptor. Khan S, Tyson AS et al. Nature. 2025 Dec 18;648(8094):755–763.
Bottom-up design of Ca2+ channels from defined selectivity filter geometry. Liu Y, Weidle C et al. Nature. 2025 Dec 11;648(8093):468–476.
Molecular insights into species-specific ACE2 recognition of coronavirus HKU5. Zhang Y, Li Y et al. Nat Commun. 2025 Dec 4;16(1):10889.
Structural and functional characterization of a metagenomically derived γ-type carbonic anhydrase and its engineering into a hyperthermostable esterase. Bodourian CS, Imran M et al. Protein Sci. 2025 Dec;34(12):e70396.
Noncanonical agonist-dependent and -independent arrestin recruitment of GPR1. Cai H, Lin X et al. Science. 2025 Nov 20;390(6775):eadt8794.
Previously featured citations...Chimera Search
Google™ SearchNews
September 22, 2025
Mac users may wish to defer upgrading to MacOS Tahoe. Currently on that OS the Chimera graphics window is shifted so that it covers the command and status lines.
March 6, 2025
Chimera production release 1.19 is now available, fixing the ability to fetch structures from the PDB (details...).
December 25, 2024

|
Upcoming Events

UCSF Chimera is a program for the interactive visualization and analysis of molecular structures and related data, including density maps, trajectories, and sequence alignments. It is available free of charge for noncommercial use. Commercial users, please see Chimera commercial licensing.
We encourage Chimera users to try ChimeraX for much better performance with large structures, as well as other major advantages and completely new features in addition to nearly all the capabilities of Chimera (details...).
Chimera is no longer under active development. Chimera development was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health (P41-GM103311) that ended in 2018.
Feature Highlight
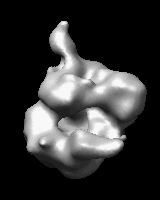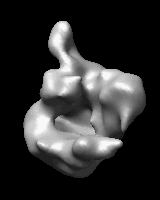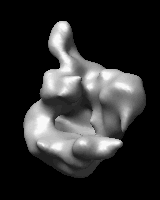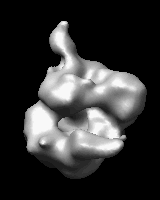
Related density maps can be compared by morphing from one to the other. Several intermediate maps are generated by interpolating between the starting and ending maps. The morph can be viewed interactively and recorded as a movie. The contour level can be adjusted automatically to keep the enclosed volume constant throughout the morph, and other aspects of map display can be adjusted with Volume Viewer.
(More features...)
Gallery Sample
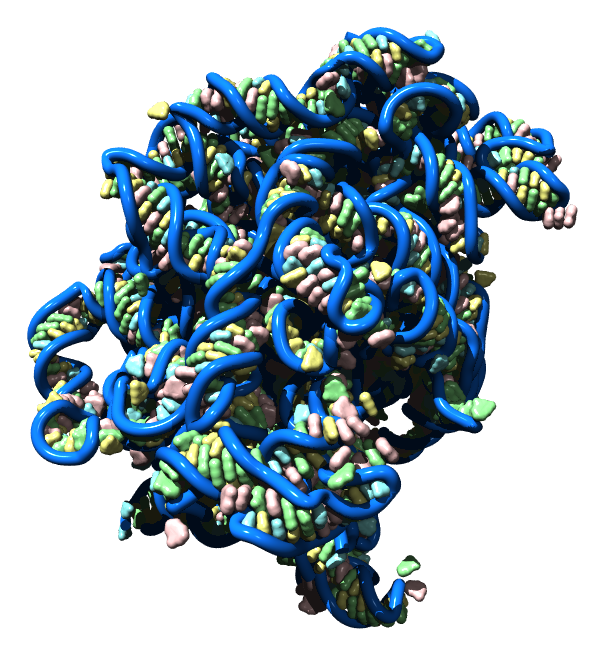
Large ribosomal RNA is shown with individual bases depicted using solvent excluded molecular surfaces. Bases A, C, G, U are colored red, yellow, green, and blue. The surfaces were made with the Chimera multiscale tool in combination with the nucleic acid blobs plug-in. The image was raytraced using POVray.
Protein Data Bank model 1s72.
(More samples...)About RBVI | Projects | People | Publications | Resources | Visit Us
Copyright 2018 Regents of the University of California. All rights reserved.