

 about
projects
people
publications
resources
resources
visit us
visit us
search
search
about
projects
people
publications
resources
resources
visit us
visit us
search
search
Quick Links
Featured Citations
In situ structural mechanism of epothilone-B-induced CNS axon regeneration. Bodakuntla S, Taira K et al. Nature. 2025 Dec 11;648(8093):477–487.
Synthetic α-synuclein fibrils replicate in mice causing MSA-like pathology. Burger D, Kashyrina M et al. Nature. 2025 Dec 11;648(8093):409-417.
Multiscale structure of chromatin condensates explains phase separation and material properties. Zhou H, Huertas J et al. Science. 2025 Dec 4;390(6777):eadv6588.
Mechanism of conductance control and neurosteroid binding in NMDA receptors. Kang H, Steigerwald R et al. Nature. 2025 Dec 4;648(8092):220–228.
Membrane-forming phospholipids allosterically modulate native-state prolyl isomerization in a CNG channel. Newton AJ, Latvala RD et al. Protein Sci. 2025 Dec;34(12):e70383.
More citations...News
November 21, 2025
The ChimeraX 1.11 release candidate is available – please try it and report any issues. See the change log for what's new. This will be the last release to support Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 and its derivatives.
July 24, 2025
ChimeraX 1.10.1 is now available, fixing the problem in 1.10 of repeat registration requests to some users.
June 26, 2025
The ChimeraX 1.10 production release is available! See the change log for what's new.
Previous news...Upcoming Events
UCSF ChimeraX (or simply ChimeraX) is the next-generation molecular visualization program from the Resource for Biocomputing, Visualization, and Informatics (RBVI), following UCSF Chimera. ChimeraX can be downloaded free of charge for academic, government, nonprofit, and personal use. Commercial users, please see ChimeraX commercial licensing.
ChimeraX is developed with support from National Institutes of Health R01-GM129325.
 ChimeraX on Bluesky:
@chimerax.ucsf.edu
ChimeraX on Bluesky:
@chimerax.ucsf.edu
Feature Highlight
|
|
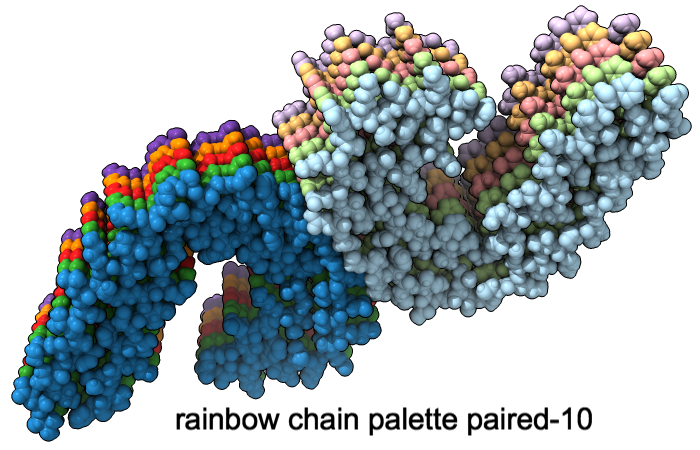
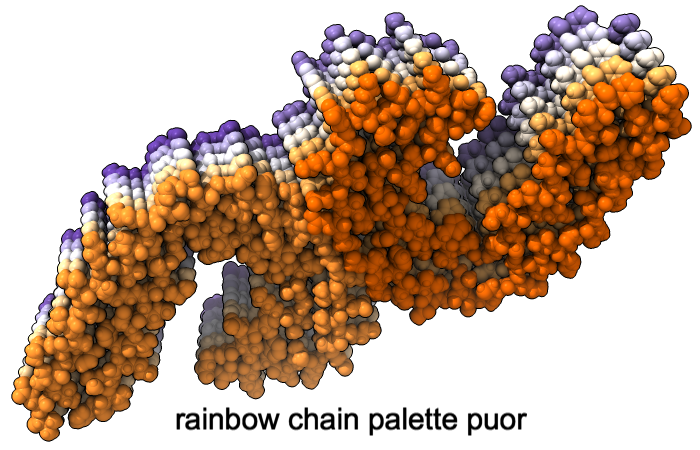
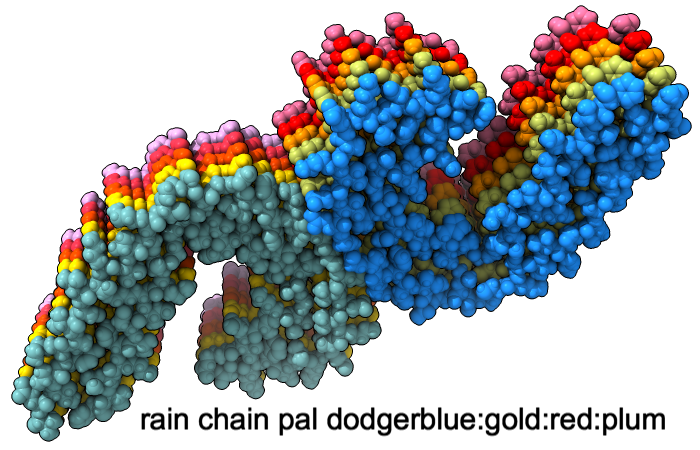
A “palette” or ordered series of colors is used to color items sequentially (rainbow) or by values such as density. The ten chains in PDB 5o3l (paired tau filament) have been colored with the commands shown as 2D labels in the images. The first two examples at left use predefined palettes (credit to www.ColorBrewer.org, color specifications and designs by Cynthia A. Brewer, Pennsylvania State University), whereas the third shows specifying colors individually.
 More features...
More features...
Example Image
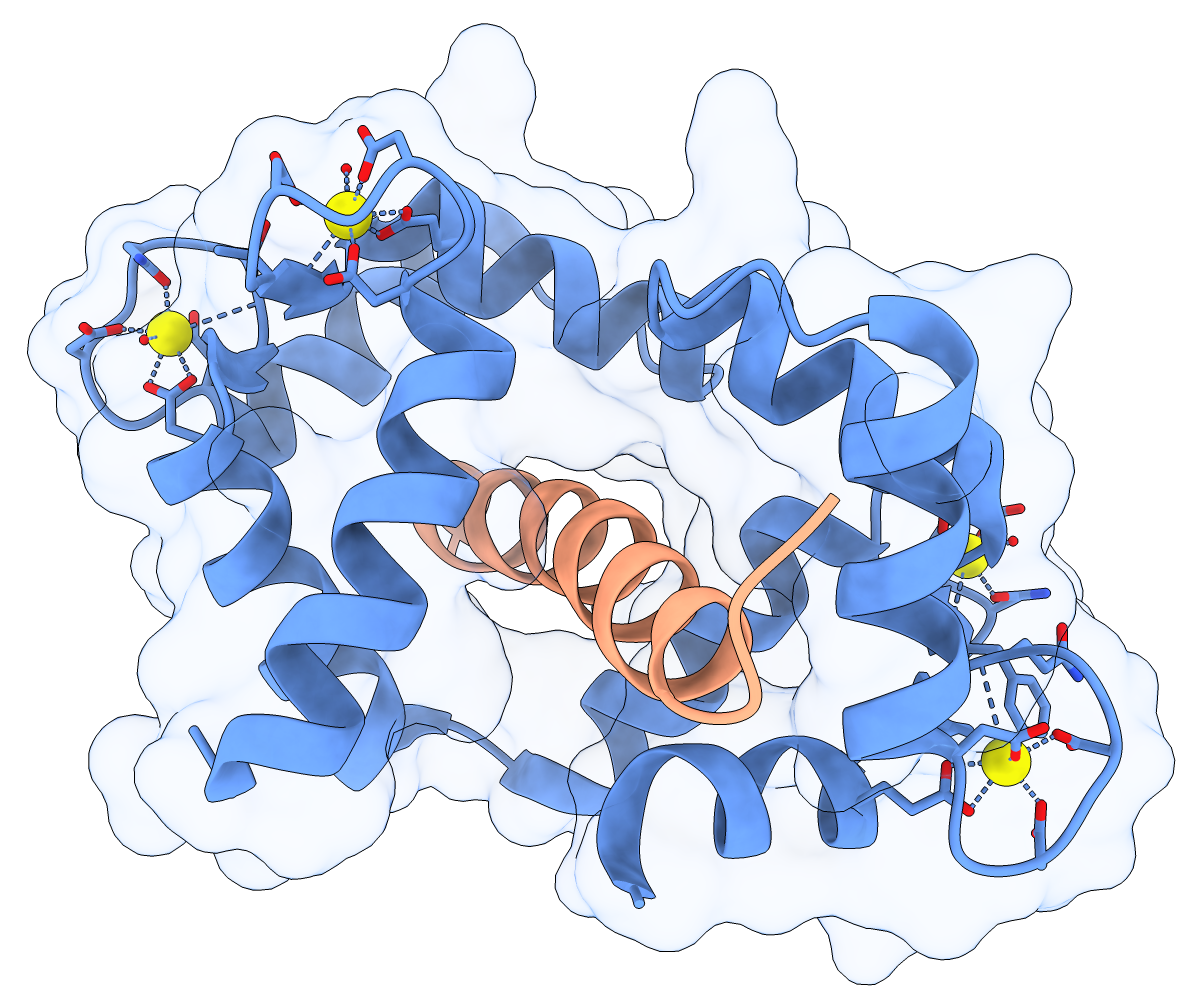
Calmodulin (CaM) acts as a calcium sensor. When its four Ca++ sites are fully occupied, it binds and modulates the activity of various downstream proteins, including CaM-dependent protein kinase I (CaMKI). Here, a complex between CaM and its target peptide from CaMKI (PDB 1mxe) is shown with cartoons, a transparent molecular surface, silhouette outlines, and light soft ambient occlusion. (If you prefer a less smudgy/rustic appearance, try using light gentle instead.) For image setup other than positioning, see the command file cam.cxc.
About RBVI | Projects | People | Publications | Resources | Visit Us
Copyright 2018 Regents of the University of California. All rights reserved.